1. 窗口函数
-
窗口函数,也叫 OLAP 函数(Online Anallytical Processing,联机分析处理),可以对数据库数据进行实时分析处理。
- 基本语法
<窗口函数> over (partition by <用于分组的列名> order by <用于排序的列名>) - 窗口函数分类
- 专用窗口函数,包括 rank, dense_rank, row_number 等专用窗口函数;
- 聚合函数,如 sum、avg、count、max、min 等;
- 因为窗口函数是对 where 或者 group by 子句处理后的结果进行操作,所以窗口函数原则上只能写在 select 子句中。
2. 窗口函数 VS GROUP BY
-
窗口函数具备了我们之前学过的 group by 子句分组的功能和 order by 子句排序的功能,但是二者具有完全不同的应用场景。
-
窗口函数有以下功能:
- 同时具有分组和排序的功能
- 不减少原表的行数
3. RANK
-
语法
select *, rank() over (partition by 分组字段 order by 排序字段 desc) as ranking from table- partition by 用来对表分组;
- order by 子句的功能是对分组后的结果进行排序;
-
示例
select *, rank() over (partition by t.department_id order by t.salary_amount desc) as ranking from ( SELECT s.employee_id,e.employee_name,e.department_id as department_id,s.salary_amount FROM test.employee e join test.salary s on s.employee_id=e.employee_id ) t;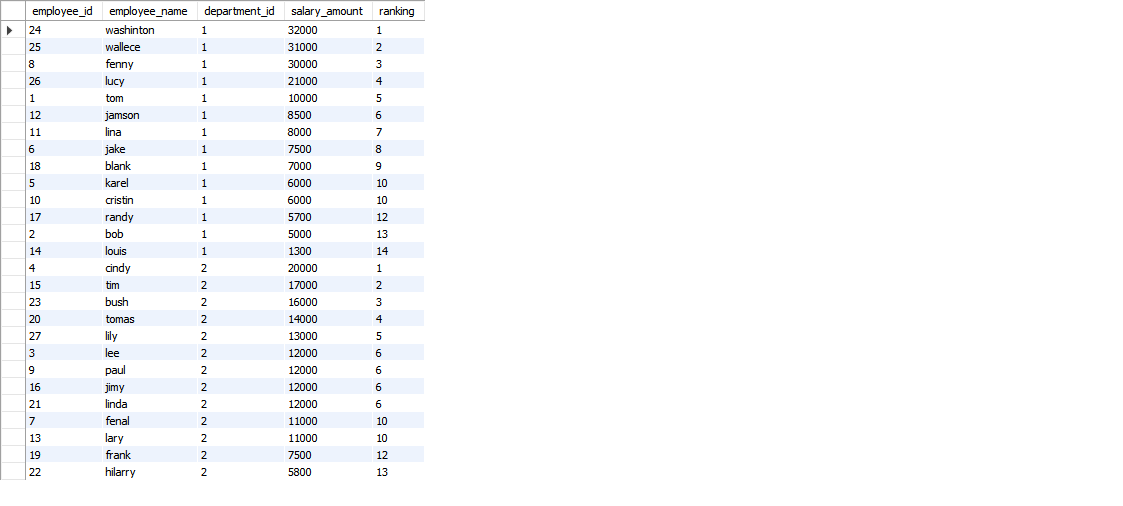
4. DENSE RANK
-
dense_rank,排序时会将相同值的排名排为同一个值;
-
语法
select *, dense_rank() over (partition by 分组字段 order by 排序字段 desc) as ranking from table- partition by 用来对表分组;
- order by 子句的功能是对分组后的结果进行排序;
-
示例
select *, dense_rank() over (partition by t.department_id order by t.salary_amount desc) as ranking from ( SELECT s.employee_id,e.employee_name,e.department_id as department_id,s.salary_amount FROM test.employee e join test.salary s on s.employee_id=e.employee_id ) t;
窗口聚合函数
- 示例
select *, sum(salary_amount) over (partition by t.department_id) as dep_sum_salary, avg(salary_amount) over (partition by t.department_id) as dep_avg_salary, count(salary_amount) over (partition by t.department_id) as dep_count, max(salary_amount) over (partition by t.department_id) as dep_max_salary, from ( SELECT s.employee_id,e.employee_name,e.department_id as department_id,s.salary_amount FROM test.employee e join test.salary s on s.employee_id=e.employee_id ) t;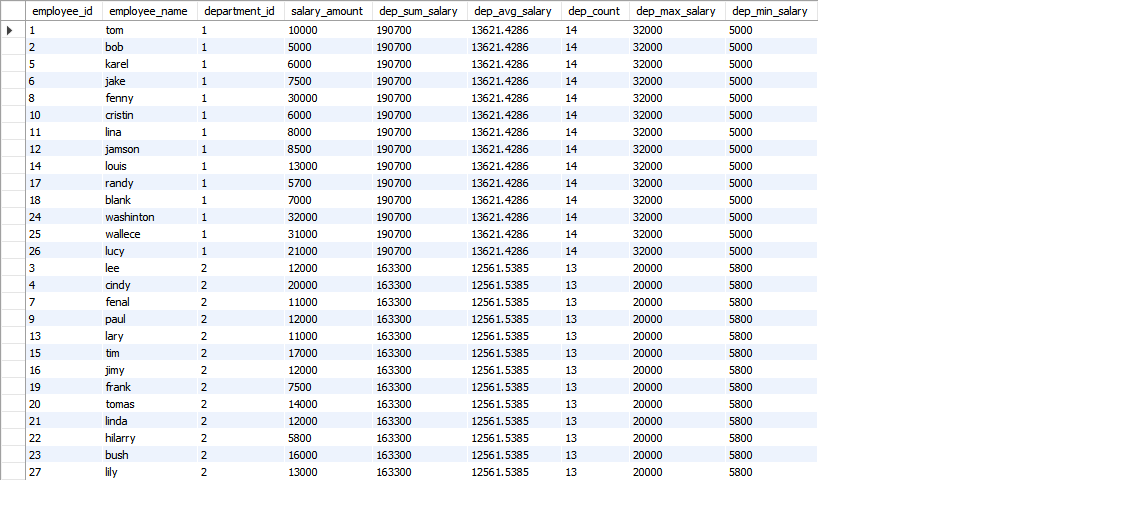
TOP N 问题
-
示例
select * from ( -- 注意:这里需要使用嵌套才能使用排名字段 select *, dense_rank() over (PARTITION by t.department_id order by t.salary_amount desc) as 排名 from ( SELECT s.employee_id,e.employee_name,e.department_id as department_id,s.salary_amount FROM test.employee e join test.salary s on s.employee_id=e.employee_id ) t ) t1 where t1.排名<=10 ;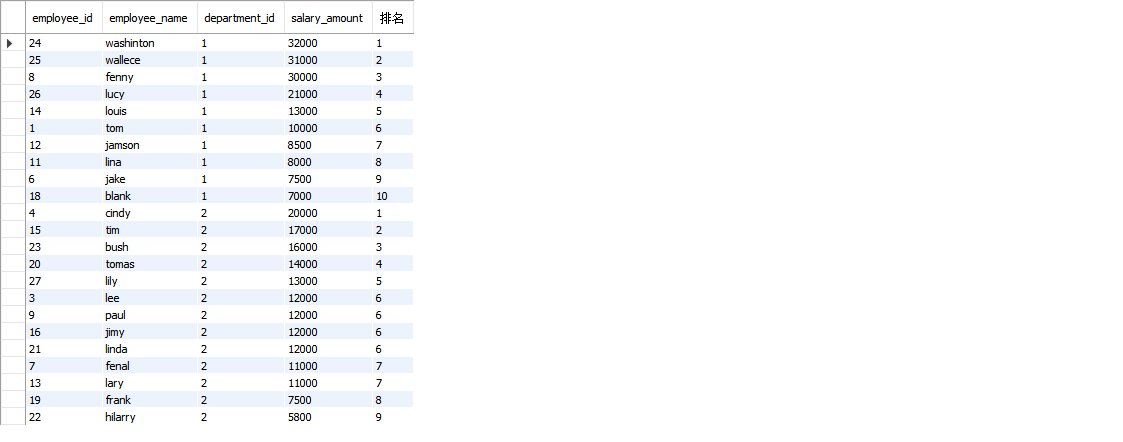
组内比较问题
-
示例
select * from ( select *, avg(salary_amount) over (partition by t.department_id) as dep_avg_salary from ( SELECT s.employee_id,e.employee_name,e.department_id as department_id,s.salary_amount FROM test.employee e join test.salary s on s.employee_id=e.employee_id ) t ) t1 where t1.salary_amount>=t1.dep_avg_salary ;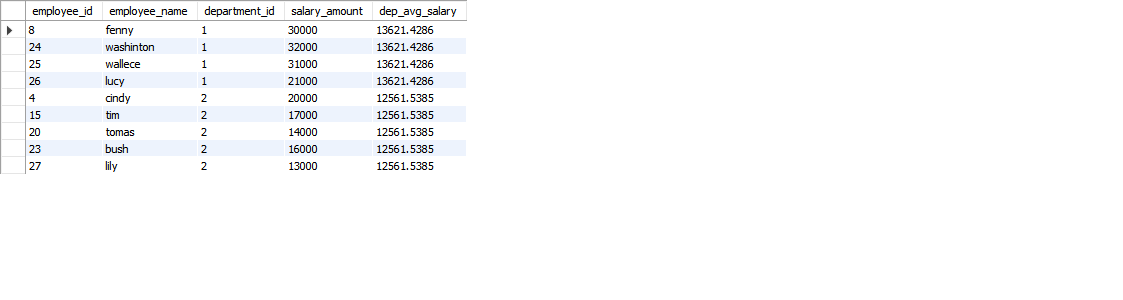
PRECEDING
- 往前 n 行数据
最近 N (小时/天/周/月)平均统计问题
- 示例:
-
查找不同产品每个月销量、以及截至当前月最近3个月的平均销售额;
SELECT m.product,m.ym,m.amount, AVG(m.amount) OVER( PARTITION BY m.product ORDER BY m.ym ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW ) FROM sales_monthly m ORDER BY m.product,m.ym- AVG 函数 OVER 子句中的 PARTITION BY 选项表示按照产品进行分区。
- ORDER BY选项表示按照月份进行排序;
- ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW 表示窗口从当前行的前2行开始,直到当前行结束。
-
FOLLOWING
- 往后 n 行数据
- 使用方法,与 PRECEDING 类似,只不过对象是统计到当前行开始往后。
UNBOUNDED
- UNBOUNDED PRECEDING 表示从前面的起点;
累计求和问题(ROWS BETWEEN)
- 示例:
-
查找不同产品截至当前月份的累计销售额
SELECT m.product,m.ym,m.amount, SUM(m.amount) OVER( PARTITION BY m.product ORDER BY m.ym ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW ) FROM sales_monthly m ORDER BY m.product,m.ym- SUM函数OVER子句中的PARTITION BY选项表示按照产品进行分区。
- ORDER BY选项表示按照月份进行排序。
- ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW 表示窗口从当前分区第1行开始,直到当前行结束。
-
- UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING 表示到后面的终点。
累计求和问题(RANGE BETWEEN)
- 示例:
-
查找短期之内(5天)累计转账超过100万元的账户。
SELECT log_ts,from_user,total_amount FROM ( SELECT to_char(t.log_ts,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') log_ts,t.from_user,t.amount, SUM(t.amount) OVER( PARTITION BY t.from_user ORDER BY t.log_ts RANGE INTERVAL '5' DAY PRECEDING ) AS total_amount FROM transfer_log t WHERE t.type = '转账' ) WHERE total_amount >= 1000000;
-
LAG
- 往前第 n 行数据
- 语法:
Lag ( scalar_expression [ ,offset ] , [ default ] ) OVER ( [ partition_by_clause ] order_by_clause )
去年同期问题
TODO
LEAD
- 往后第 n 行数据
- 基本语法:
LAG( 想要的返回值(可以是各种函数) [,偏移量(从1开始)] [,如果偏移后没有选定的行,则返回的默认值]) OVER ( [ partition_by 分区 ] order_by 顺序 ) - 高级语法:
lag(列名,1,0) over (partition by 分组列 order by 排序列 rows between 开始位置 preceding and 结束位置 following)
用户访问时长问题
- 有一个日志登陆列表,获取用户在某个页面停留时长
+------------------+----------------------+---------------+--+ | userid | time | url | +------------------+----------------------+---------------+--+ | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:10:00 | url1 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:15:10 | url2 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:16:40 | url3 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 02:13:00 | url4 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 03:14:30 | url5 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:10:00 | url1 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:15:10 | url2 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:16:40 | url3 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 02:13:00 | url4 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 03:14:30 | url5 | +------------------+----------------------+---------------+--+ - 代码
select userid ,time ,UNIX_TIMESTAMP( lead(time,1) over(partition by userid order by time),'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss' ) - UNIX_TIMESTAMP( time,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss' ) as period ,url from user_log - 结果
+---------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+--+ | userid | stime | etime | period | url | +---------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+--+ | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:10:00 | 2015-11-12 01:15:10 | 310 | url1 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:15:10 | 2015-11-12 01:16:40 | 90 | url2 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 01:16:40 | 2015-11-12 02:13:00 | 3380 | url3 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 02:13:00 | 2015-11-12 03:14:30 | 3690 | url4 | | Marry | 2015-11-12 03:14:30 | NULL | NULL | url5 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:10:00 | 2015-10-12 01:15:10 | 310 | url1 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:15:10 | 2015-10-12 01:16:40 | 90 | url2 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 01:16:40 | 2015-10-12 02:13:00 | 3380 | url3 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 02:13:00 | 2015-10-12 03:14:30 | 3690 | url4 | | Peter | 2015-10-12 03:14:30 | NULL | NULL | url5 | +---------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+--+
连续登录问题
- 寻找至少连续出现3次的数字
+--------------+----+ | id |num | +--------------+----+ | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 1 | | 5 | 2 | | 6 | 2 | | 7 | 3 | | 8 | 3 | | 9 | 3 | | 10 | 4 | +--------------+----+ - 思路:增加两列,使用lag函数-把下面的数据往上错位一个,错位2个,判断num和错位的两列是否相等
- 代码
select id ,distinct num from ( select id ,num ,lag(num,1) over(partition by id) as lag1 ,lag(num,2) over(partition by id) as lag2 from log_table ) a where num=lag1 and lag1=lag2
用户先后进行某项操作问题
- 统计每天符合以下条件的用户数:
- A 操作(opr_id)之后是 B 操作,AB 操作必须相邻
select date,count(*) from( select user_id from( select user_id, convert(log_time,date) date, opr_id f, lag(opr_id,1) over( partition by user_id,convert(log_time,date) order by log_time ) l from tracking_log ) a where f='A' and l='B' ) b group by date;
最近 N 天(小时/周/月)重复行为问题
-
获取在 48 小时之内重复的记录
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT b.* , LAG(b.OperatorTime, 1, b.OperatorTime) OVER ( PARTITION BY b.No ORDER BY b.OperatorTime ) AS BeforTime , LEAD(b.OperatorTime, 1, b.OperatorTime) OVER ( PARTITION BY b.No ORDER BY b.OperatorTime ) AS NextTime FROM Test b ) a WHERE DATEDIFF(HH, a.BeforTime, a.OperatorTime) < 24 AND DATEDIFF(HH, a.OperatorTime, a.NextTime) < 24 AND a.No IN ( SELECT c.No FROM dbo.Test c GROUP BY c.No HAVING COUNT(c.No) > 1 )
NTILE(n)
- 把有序分区中的行分发到指定数据的组中,各个组有编号,编号从1开始,对于每一行,NTILE 返回此行所属的组的编号。
- 注意:n 必须为 int 类型。
GROUP_CONCAT
-
示例 1:
- 有下面的数据表,要求按分数 score 进行分组,并将分组后的学生姓名打印下来;
|id |subject |student|teacher|score| --------------------------------------- |1 |数学 |小红 |王老师 |80 | |2 |数学 |小李 |王老师 |80 | |3 |数学 |小王 |王老师 |70 | |4 |数学 |小张 |王老师 |90 | |5 |数学 |小赵 |王老师 |70 | |6 |数学 |小孙 |王老师 |80 | |7 |数学 |小钱 |王老师 |90 | |8 |数学 |小高 |王老师 |70 | |9 |数学 |小秦 |王老师 |80 | |10 |数学 |小马 |王老师 |90 | |11 |数学 |小朱 |王老师 |90 | |12 |语文 |小高 |李老师 |70 | |15 |语文 |小秦 |李老师 |70 | |18 |语文 |小马 |李老师 |80 | |21 |语文 |小朱 |李老师 |90 | |24 |语文 |小钱 |李老师 |90 | -
代码:
select score,group_concat(student) from exam group by score; -
执行结果为
|score |group_concat(student) | ------------------------------------- |70 |小王,小赵,小高,小高,小秦 | |80 |小红,小李,小孙,小秦,小马 | |90 |小张,小钱,小马,小朱,小朱,小钱 | - 如果我们需要去重,则需要给函数中加一个distinct参数:
select score,group_concat(distinct student) from exam group by score;-
执行结果为:
|score |group_concat(student) | --------------------------------- |70 |小王,小赵,小高,小秦 | |80 |小红,小李,小孙,小秦,小马 | |90 |小张,小钱,小马,小朱 |
- 有下面的数据表,要求按分数 score 进行分组,并将分组后的学生姓名打印下来;
-
示例 2:
- 统计用户行为序列为 A-B-D 的用户数
- 其中:A-B 之间可以有任何其他浏览记录(如 C、E 等);
- B-D 之间除了 C 记录可以有任何其他浏览记录(如 A、E 等)。
select count(*) from( select user_id,group_concat(opr_id) ubp from tracking_log group by user_id ) a where ubp like '%A%B%D%' and ubp not like '%A%B%C%D%'
- 统计用户行为序列为 A-B-D 的用户数
参考链接
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34280060/article/details/123130155