WITH RECURSIVE 用法
- WITH xxxx AS () 是对一个查询子句做别名,同时数据库会对该子句生成临时表;
- WITH RECURSIVE 则是一个递归的查询子句,他会把查询出来的结果再次代入到查询子句中继续查询;
- 如下面的语句:
WITH RECURSIVE number(n, fact) AS ( -- 递归开始的第一条记录,只要这个这条语句一执行,就会将第一条记录了的结果存储到 number 这种表中,此时可以理解为 number 只有一条记录 SELECT 0,1 FROM DUAL UNION ALL -- UNION ALL 语句执行的结果,会和之前的执行结果一起,写入到返回结果中,这里的 n 就是 number 执行时传入的参数; SELECT n+1, (n+1)*fact FROM number WHERE n < 7 -- 只要 n < 7 条件成立,该递归就会一直执行下去; ) SELECT * FROM number; -
执行结果:
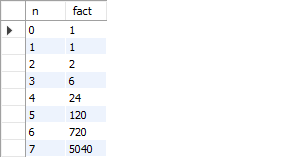
模拟销售数据需求:
- 创建 products、sales 表,并写入模拟销售数据;
-
创建 products
create table products( product_id integer not null primary key, product_name varchar(100) not null unique, product_subcategory varchar(100) not null, product_category varchar(100) not null ); - 创建 sales
create table sales( product_id integer not null, sale_time timestamp not null, quantity integer not null );
写入模拟销售数据
insert into sales
with recursive s(product_id, sale_time, quantity) as (
select product_id, '2022-04-01 00:00:00', floor(10*rand(0)) from products
union all
select product_id, sale_time + interval 1 minute, floor(10*rand(0))
from s
where sale_time < '2022-04-01 10:00:00'
)
select * from s;
-
得到结果