1. Hive 数据加载
1.1. hadoop fs -put 上传数据
- 上传文件至 master 服务器
- put 文件至 hdfs
hadoop fs -put ./archer.txt /user/hive/warehouse/test.db/team_ace_player官方不推荐使用这种方式,因为真个操作并未经过 hive,官方推荐 load 加载数据的方式上传。
1.2. load 加载
- 加载是指将数据文件移动到与 Hive 表对应的位置,移动时是纯复制、移动操作;
- 在数据 load 加载到表中时,Hive 不会对表中的数据内容进行任何转换,任何操作。
- filepath
- filepath 表示待移动数据的路径。可以指向文件(在这种情况下,Hive 将文件移动到表中),也可以指向目录(在这种情况下,Hive 将把该目录中的所有文件移动到表中)。
- filepath 文件路径支持下面三种形式,要结合 LOCAL 关键字一起考虑:
- 相对路径
- 例如:
project/data1;
- 例如:
- 绝对路径
- 例如:
/user/hive/project/data1;
- 例如:
- 具有 schema 的完整 URI
- 例如:
hdfs://namenode:9000/user/hive/project/data1。
- 例如:
- 相对路径
1.3. load 本地复制(LOCAL)
- 从本地加载数据 数据位于HS2(hadoop102)本地文件系统;
- 执行复制操作,原始文件会继续保留;
- 本质是
hadoop fs -put上传操作; - 指定 LOCAL,表示在本地文件系统中查找文件路径;
- 若指定相对路径,将相对于用户的当前工作目录进行解释;
- 用户也可以为本地文件指定完整的URI
- 例如:file:///user/hive/project/data1。
- 建表 student_local
create table student_local(num int,name string,sex string,age int,dept string) row format delimited fields terminated by ','; - 上传文件至 hadoop102
/home目录下 - 加载
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/students.txt' INTO TABLE student_local; - 查看数据
select * from student_local;
1.4. load 移动
- 从 HDFS 加载数据 数据位于 HDFS 文件系统根目录下 本质是
hadoop fs -mv移动操作;- 原始本地文件移动后,就会被删除;
- 没有指定 LOCAL 关键字。
- 如果 filepath 指向的是一个完整的 URI,会直接使用这个 URI;
- 如果没有指定 schema,Hive 会使用在 hadoop 配置文件中参数 fs.default.name 指定的(不出意外,都是 HDFS)
- 建表 student_HDFS
create external table student_HDFS(num int,name string,sex string,age int,dept string) row format delimited fields terminated by ','; - 上传文件至 hadoop102
/home目录下 -
先把数据上传到 HDFS 上
hadoop fs -put /root/hivedata/students.txt / - 加载
LOAD DATA INPATH '/students.txt' INTO TABLE student_HDFS; - 查看数据
select * from student_local;
2. Hive 插入数据
- 创建一张目标表 student_from_insert
create table student_from_insert(num int,name string,sex string,age int,dept string); - 使用
insert+select插入数据到新表中insert into table student_from_insert select num,name,sex,age,dept from student_local;
3. Hive 查询语句
3.1. Hive SQL select语法介绍
- select 基本使用
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [LIMIT [offset,] rows];--查询所有字段或者指定字段 select * from t_usa_covid19; select county, cases, deaths from t_usa_covid19;3.2. select_expr、ALL DISTINCT 结果返回与去重
- select_expr
--返回所有匹配的行 select state from t_usa_covid19; --相当于 select all state from t_usa_covid19; - DISTINCT
--返回所有匹配的行 去除重复的结果 select distinct state from t_usa_covid19; --多个字段distinct 整体去重 select distinct county,state from t_usa_covid19;
3.3. WHERE 过滤
- 在 WHERE 表达式中,可以使用 Hive 支持的任何函数和运算符;
-
但聚合函数除外,WHERE 关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用
-
WHERE 语法
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [LIMIT [offset,] rows]; -
示例
select * from t_usa_covid19 where 1 > 2; -- 1 > 2 返回false select * from t_usa_covid19 where 1 = 1; -- 1 = 1 返回true --找出来自于California州的疫情数据 select * from t_usa_covid19 where state = "California"; --where条件中使用函数 找出州名字母长度超过10位的有哪些 select * from t_usa_covid19 where length(state) >10 ; --注意:where条件中不能使用聚合函数 -- --报错 SemanticException:Not yet supported place for UDAF ‘sum' --聚合函数要使用它的前提是结果集已经确定。 --而where子句还处于“确定”结果集的过程中,因而不能使用聚合函数。 select state,sum(deaths) from t_usa_covid19 where sum(deaths) >100 group by state; --可以使用Having实现 select state,sum(deaths) from t_usa_covid19 group by state having sum(deaths) > 100;
3.4. 聚合操作
-
聚合(Aggregate)操作函数,如:Count、Sum、Max、Min、Avg 等函数。
-
聚合函数的最大特点是不管原始数据有多少行记录,经过聚合操作只返回一条数据,这一条数据就是聚合的结果。
-
WHERE 关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用
-
常见的聚合操作函数:
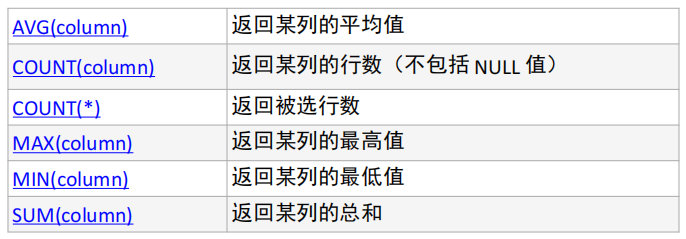
-
示例
--统计美国总共有多少个县county select count(county) from t_usa_covid19; --统计美国加州有多少个县 select count(county) from t_usa_covid19 where state = "California"; --统计德州总死亡病例数 select sum(deaths) from t_usa_covid19 where state = "Texas"; --统计出美国最高确诊病例数是哪个县 select max(cases) from t_usa_covid19;
3.5. GROUP BY 分组
- GROUP BY 语句用于结合聚合函数,根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组;
-
如果没有group by语法,则表中的所有行数据当成一组。
-
GROUP BY 语法
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [LIMIT [offset,] rows]; -
示例
--根据state州进行分组 统计每个州有多少个县county select count(county) from t_usa_covid19 where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state; --想看一下统计的结果是属于哪一个州的 select state,count(county) from t_usa_covid19 where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state; -- 出现在 GROUP BY 中 select_expr 的字段:要么是 GROUP BY分组的字段,要么是被聚合函数应用的字段。 select state,count(county),sum(deaths) from t_usa_covid19 where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state;
3.6. HAVING 分组后过滤
- 在 SQL 中增加 HAVING 子句原因是,WHERE 关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用。
- 原因:聚合计算是在 group by 分组之后进行,而 where 需要在分组前过滤。where 是一个确定结果的过程,group by 是在确定结果基础上执行。
-
HAVING 子句可以让我们筛选分组后的各组数据,并且可以在 Having 中使用聚合函数,因为此时 where,group by 已经执行结束,结果集已经确定。
- HAVING 与 WHERE 区别
- having是在分组后对数据进行过滤
- where是在分组前对数据进行过滤
- having后面可以使用聚合函数
- where后面不可以使用聚合函数
-
示例
--先where分组前过滤,再进行group by分组, 分组后每个分组结果集确定 再使用having过滤 select state,sum(deaths) from t_usa_covid19 where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state having sum(deaths) > 10000; --这样写更好 即在group by的时候聚合函数已经作用得出结果 having直接引用结果过滤 不需要再单独计算一次了 select state,sum(deaths) as cnts from t_usa_covid19 where count_date = "2021-01-28" group by state having cnts> 10000;
3.7. ORDER BY 排序
-
ORDER BY 语法
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ... FROM table_reference [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY col_list] [ORDER BY col_list] [LIMIT [offset,] rows]; -
示例
--根据确诊病例数升序排序 查询返回结果 select * from t_usa_covid19 order by cases; --不写排序规则 默认就是asc升序 select * from t_usa_covid19 order by cases asc; --根据死亡病例数倒序排序 查询返回加州每个县的结果 select * from t_usa_covid19 where state = "California" order by cases desc;
4. Hive Join 使用
- 根据数据库的三范式设计要求和日常工作习惯来说,我们通常不会设计一张大表把所有类型的数据都放在一起,而 是不同类型的数据设计不同的表存储。
- 在这种情况下,有时需要基于多张表查询才能得到最终完整的结果;join语法的出现是用于根据两个或多个表中的列之间的关系,从这些表中共同组合查询数据。
- 在Hive中,使用最多,最重要的两种join分别是:
- inner join(内连接)
- left join(左连接)
5. Hive SQL 常用函数
SQL 函数类型
- 使用
show functions查看当下可用的所有函数; -
通过
describe function extended funcname来查看函数的使用方式。 - 内置函数可分为:数值类型函数、日期类型函数、字符串类型函数、集合函数、条件函数等;
- 用户定义函数根据输入输出的行数可分为3类:
- UDF(User-Defined-Function)普通函数,一进一出;
- UDAF(User-Defined Aggregation Function)聚合函数,多进一出;
- UDTF(User-Defined Table-Generating Functions)表生成函数,一进多出。
String Functions 字符串函数
- 字符串长度函数:length
select length("itcast");
- 字符串反转函数:reverse
select reverse("itcast"); 字符串连接函数:concatselect concat("angela","baby");
-
带分隔符字符串连接函数:concat_ws(separator, [string array(string)]+) select concat_ws('.', 'www', array('itcast', 'cn'));
- 字符串截取函数:substr(str, pos[, len]) 或者 substring(str, pos[, len])
select substr("angelababy",-2); –pos是从1开始的索引,如果为负数则倒着数select substr("angelababy",2,2);
- 分割字符串函数: split(str, regex)
select split('apache hive', ' ');
Date Functions 日期函数
- 获取当前日期: current_date
select current_date();
- 获取当前UNIX时间戳函数: unix_timestamp
select unix_timestamp();
- 日期转UNIX时间戳函数: unix_timestamp
select unix_timestamp("2011-12-07 13:01:03");
- 指定格式日期转UNIX时间戳函数: unix_timestamp
select unix_timestamp('20111207 13:01:03','yyyyMMdd HH:mm:ss');
- UNIX时间戳转日期函数: from_unixtime
select from_unixtime(1618238391);select from_unixtime(0, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss');
- 日期比较函数: datediff 日期格式要求’yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss’ or ‘yyyy-MM-dd’
select datediff('2012-12-08','2012-05-09');
- 日期增加函数: date_add
select date_add('2012-02-28',10);
- 日期减少函数: date_sub
select date_sub('2012-01-1',10);
Mathematical Functions 数学函数
- 取整函数: round 返回double类型的整数值部分 (遵循四舍五入)
select round(3.1415926);
- 指定精度取整函数: round(double a, int d) 返回指定精度d的double类型
select round(3.1415926,4);
- 取随机数函数: rand 每次执行都不一样 返回一个0到1范围内的随机数
select rand();
- 指定种子取随机数函数: rand(int seed) 得到一个稳定的随机数序列
select rand(3);
Conditional Functions 条件函数
- 使用之前课程创建好的student表数据
select * from student limit 3;
- if条件判断: if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull)
select if(1=2,100,200);select if(sex ='男','M','W') from student limit 3;
- 空值转换函数: nvl(T value, T default_value)
select nvl("allen","itcast");select nvl(null,"itcast");
- 条件转换函数: CASE a WHEN b THEN c [WHEN d THEN e]* [ELSE f] END
select case 100 when 50 then 'tom' when 100 then 'mary' else 'tim' end;select case sex when '男' then 'male' else 'female' end from student limit 3;